Parkinson’s Disease
What is Parkinson’s Disease?
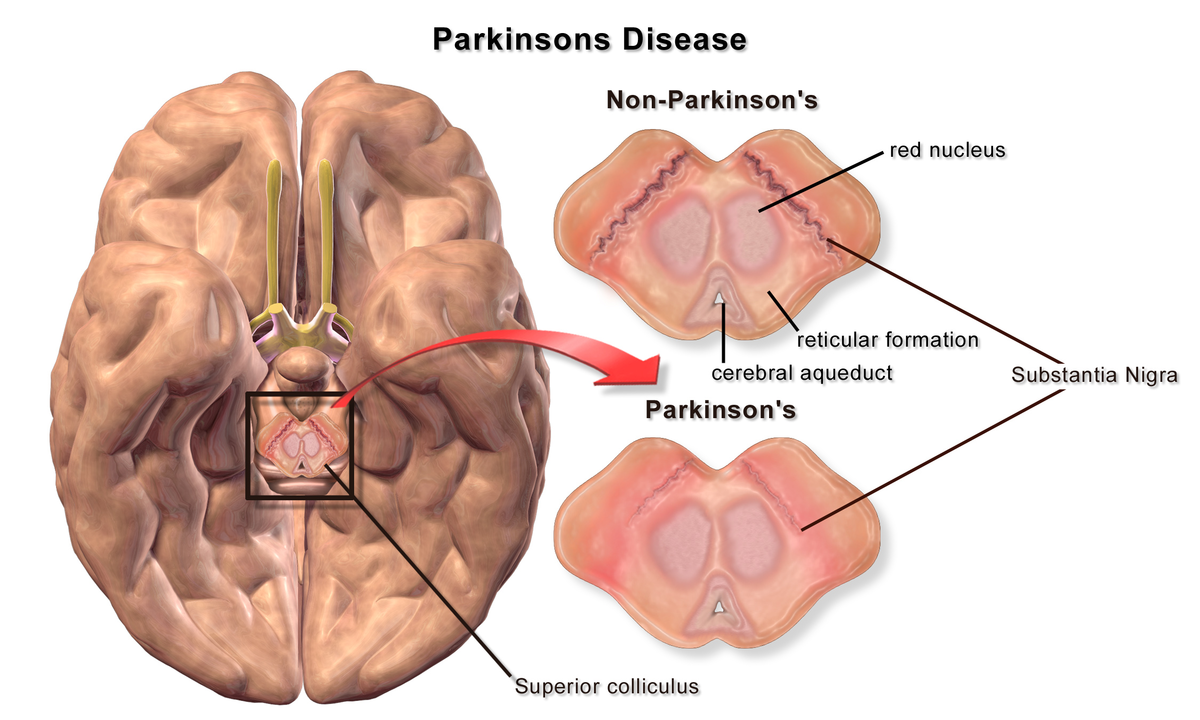
Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is a progressive neurological disorder that affects movement. It primarily results from the loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain, specifically in the substantia nigra region.
The disease usually occurs in older people, but younger people can also be affected. Men are affected more often than women.
How Parkinson’s Disease Happens:
The exact cause of Parkinson’s is unknown, but it is believed to be due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors:
Genetics
Some cases are linked to inherited gene mutations, but they are rare.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to pesticides, heavy metals, or toxins may increase the risk.
Aging
The risk increases with age, as natural dopamine production declines.
Symptoms For Parkinson’s Disease
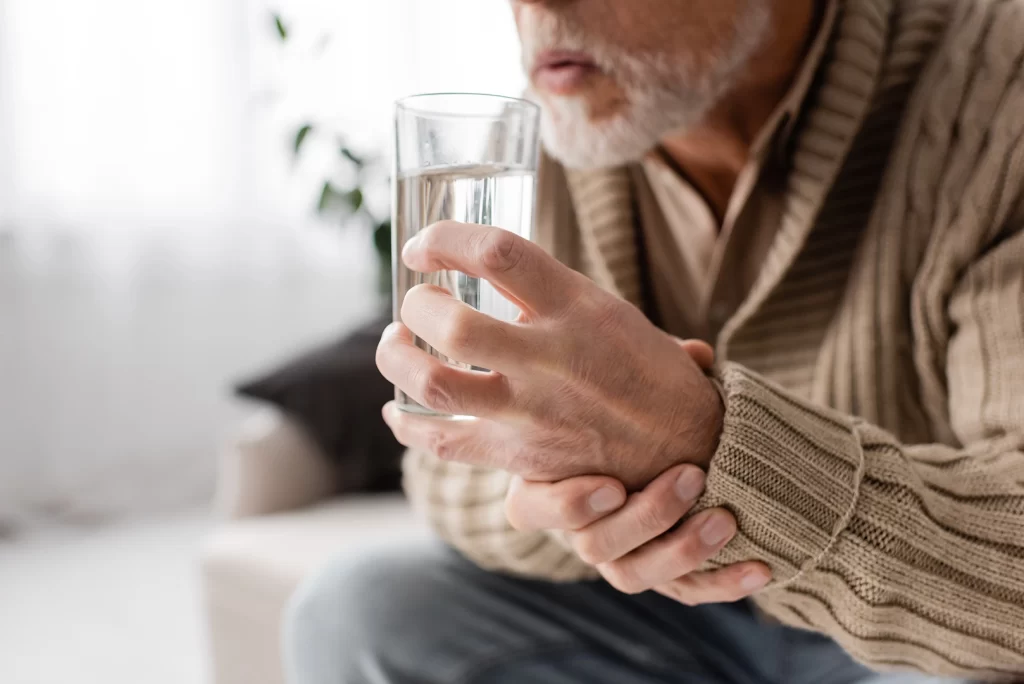
Tremors
Slowed movement
Muscle stiffness
Difficulty speaking
Sleep problems
Fatigue
Parkinson’s Disease Treatment
There is no cure for PD, but therapies and medicines can help reduce symptoms. Other treatments include surgery, physical therapy, and speech therapy.
Medication Treatments
Levodopa/carbidopa, a combination medicine that increases the amount of dopamine in the brain, is the most common medication for PD.
Doctors may use other medicines such as anticholinergics to reduce involuntary muscle movement.
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
• A surgically implanted device sends electrical impulses to specific brain areas, improving movement.
• The major advantage is that DBS is reversible, while intentional scarring damage is not. This treatment approach is almost always an option in later stages of Parkinson’s disease when levodopa therapy becomes less effective, and in people who have tremor that doesn’t seem to respond to the usual medications.
Experimental Treatments
Some of the experimental treatments could help with PE such as:
- Stem cell transplants – These add new dopamine-using neurons into your brain to take over for damaged ones.
- Neuron-repair treatments – These treatments try to repair damaged neurons and encourage new neurons to form.