Ischemic Stroke
What is Ischemic Stroke?
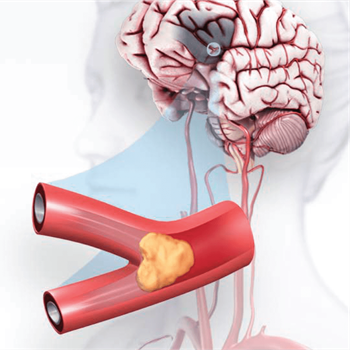
Ischemic Stroke happens when the brain’s blood vessels become narrowed or blocked. This causes reduced blood flow, known as ischemia.
It also can be caused by blood clots or other debris that travel through the bloodstream, most often from the heart. An Ischemic Stroke occurs when fatty deposits, blood clots or other debris become lodged in the blood vessels in the brain.
This deprives brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients, leading to potential brain damage if not treated quickly.
Symptoms of Ischemic Stroke:
Trouble speaking and understanding what others are saying
A person having a stroke may be confused, slur words or may not be able to understand speech.
Numbness, weakness or paralysis in the face, arm or leg
This often affects just one side of the body. Also, one side of the mouth may droop when trying to smile.
Problems seeing in one or both eyes
The person may suddenly have blurred or blackened vision in one or both eyes. Or the person may see double.
Headache
A sudden, severe headache may be a symptom of a stroke. Vomiting, dizziness and a change in consciousness may occur with the headache.
Trouble walking
Someone having a stroke may stumble or lose balance or coordination.
Ischemic Stroke Treatment
The immediate treatment for Ischemic Stroke is clot removal. Doctors can accomplish this with medication and mechanical treatments.
Medication Treatment with Intravenous (IV) Thrombolytics
e.g., tPA – Tissue Plasminogen Activator
A clot-busting drug that helps dissolve the clot if given within 4.5 hours of stroke onset.
Many people don’t arrive at the hospital in time to receive the medication, which can save lives and reduce long-term effects of stroke. So it’s important to identify stroke and seek treatment immediately.
Mechanical Treatment to Remove the Clot
A mechanical thrombectomy removes a clot in eligible patients with a large vessel occlusion, or LVO.
A catheter-based procedure where a doctor removes the clot using a stent retriever.
The procedure:
- Is usually done within six hours of the onset of acute stroke symptoms but can be done up to 24 hours after symptoms begin if imaging tests show undamaged brain tissue.
- May include medication treatment in eligible patients.
Ongoing Treatment & Recovery
Individualized hospital care for stroke focuses on many aspects of recovery, including:
- Blood Pressure Medications – Helps control hypertension to prevent future strokes.
- Physical & Speech Therapy – Helps regain movement and communication skills after brain damage.
- Lifestyle Changes – Healthy diet, exercise, quitting smoking, and controlling diabetes.