Therapeutics Area
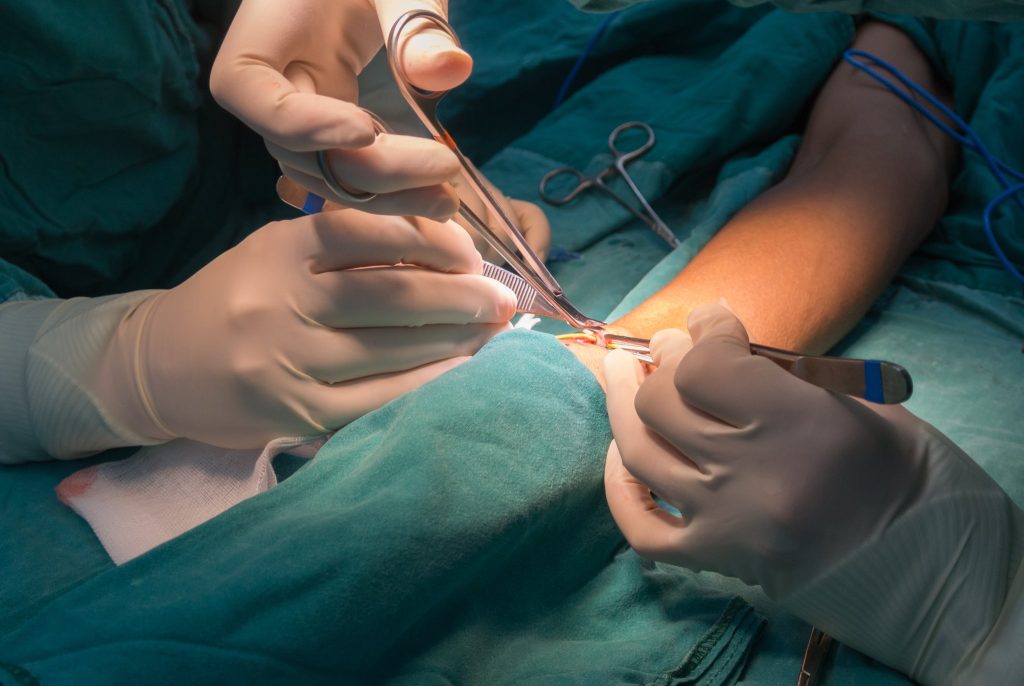
Arteriovenous Fistula/Graft
An Arteriovenous Fistula (AVF) is an abnormal connection between an artery and a vein, bypassing the capillaries.
An Arteriovenous Graft (AVG) is an artificial connection between an artery and a vein using a synthetic tube or graft.
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a condition where a blood clot (thrombus) forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs. This can be dangerous because the clot might break loose and travel to the lungs, causing a Pulmonary Embolism (PE), which can be life-threatening.
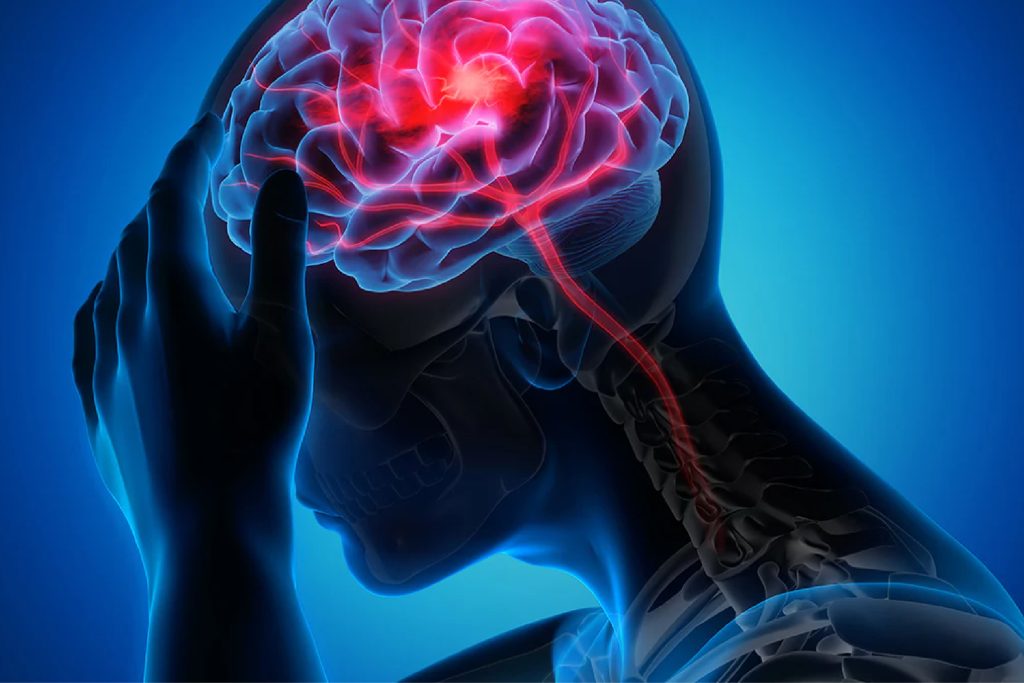
Haemorrhagic Stroke
A Haemorrhagic Stroke occurs when a weakened blood vessel in the brain ruptures, leading to bleeding (haemorrhage) in or around the brain. This bleeding can increase pressure in the brain, damaging brain cells and impairing normal function.
Ischemic Stroke
An Ischemic Stroke occurs when the blood flow to a part of the brain is blocked, usually due to a blood clot or narrowing of the arteries. This deprives brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients, leading to potential brain damage if not treated quickly.
Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary Embolism (PE) is a life-threatening condition that occurs when a blood clot (usually from the deep veins of the legs, called DVT) travels to the lungs and blocks a pulmonary artery.
Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is a progressive brain disorder that affects movement, balance, and other functions. It’s caused by the death of nerve cells in the brain.

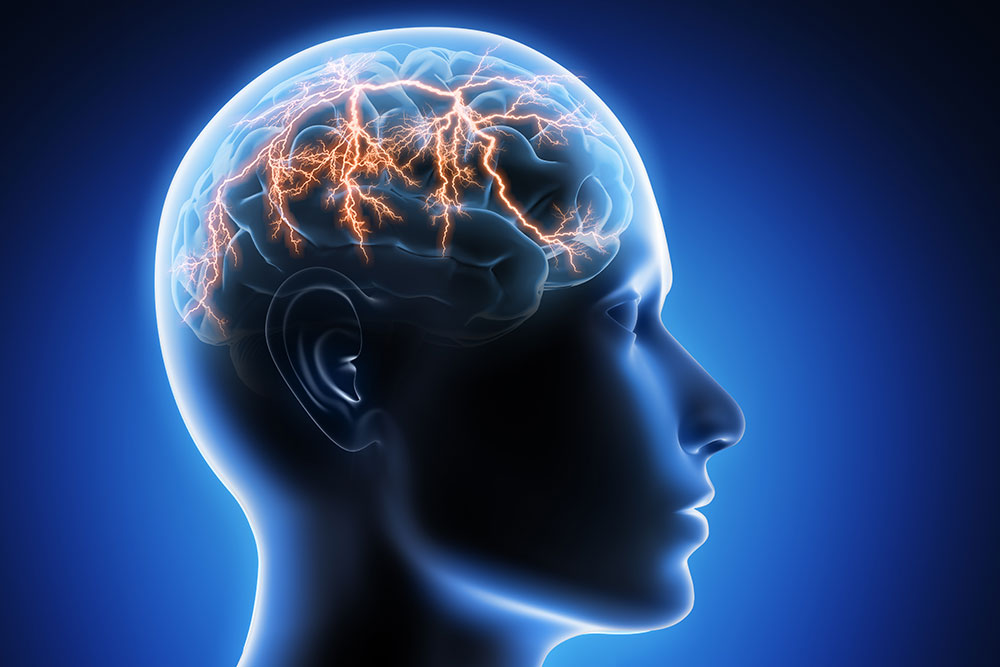
Epilepsy
Epilepsy — also known as a seizure disorder — is a brain condition that causes recurring seizures. There are many types of epilepsy. In some people, the cause can be identified. In others, the cause is not known.